News
December 2025, Introduction of decision tool starts
At Amsterdam UMC, location AMC, the introduction of the decision support tool has begun. We have collected data on key implementation determinants to guide and optimize the upcoming rollout.
November 2025, Nebulization support tool finished
The decision support tool—developed in collaboration with the Amsterdam UMC ventilation working group and grounded in the best available evidence—has been formally completed.
20 October, 2025: NEBUL-IC national survey submitted for publication
Our nationwide survey on nebulization practices has been completed and submitted for publication.

Recruitment
Recruitment of centers for the implementation phase is complete. The ICUs of Maasstad Ziekenhuis, UMC Utrecht and Noordwest Ziekenhuisgroep (Alkmaar) have confirmed their participation.

Current study phase
We are now in the introduction phase, implementing the nebulization decision tool in the first centers and assessing key determinants that will guide the full implementation.
Study Summary
Why this project?
Nebulization is widely used in invasively ventilated ICU patients, yet often without a clear clinical indication. Habits, convictions, and local routines strongly influence practice, leading to substantial variation between ICUs. Our national survey (submitted for publication) confirmed this, showing inconsistent use, differing indications, and a lack of structured decision support across Dutch ICUs.
Non-indicated nebulization offers no proven benefit, may expose patients to unnecessary risks—as demonstrated in the NEBULAE trail (JAMA), and consumes valuable staff time and materials. Improving appropriateness is therefore essential.
The NEBUL-ICU project, funded within the ZonMw Good Use of Medicines (GGG) programme, aims to ensure that nebulization is performed only when indicated. To support this, we developed a consensus-based decision support tool that helps clinicians systematically assess whether nebulization is warranted.
Scientific Foundation
The nebulization decision support tool is grounded in the best available evidence and expert consensus. As a first step, we conducted an international Delphi study to identify clear, consensus-based indications and contraindications for nebulization in invasively ventilated ICU patients (manuscript forthcoming; see published protocol here).
Building on these findings, and in close collaboration with the Amsterdam UMC ventilation working group, we developed a practical, bedside-ready decision support tool designed to promote consistent, indication-based nebulization, and promote daily reassessment of the need for nebulization. [insert picture of decision support tool].
Part of the ZonMw GGG Program
The NEBUL-ICU project is funded within the Good Use of Medicines (GGG) program of ZonMw, aimed at improving the safe, effective, and appropriate use of medications. If you want to read more about this project within the GGG program: see project deimplementation standard nebulization. Want to learn more about the GGG program itself: see Program Goed Gebruik Geneesmiddelen | ZonMw.
More details about the NEBUL-ICU Project
The goal of the NEBUL-ICU project is to improve indication-based nebulization in mechanically ventilated ICU patients by developing, implementing, and evaluating a consensus-based decision support tool that supports consistent, evidence-informed clinical decision-making.
Study Design
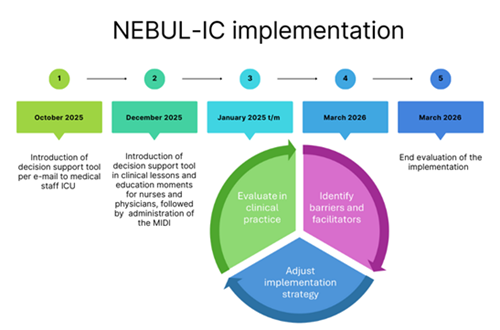
A nationwide, multi-phase implementation study consisting of four sequential components:
- Delphi Study (completed): Development of consensus-based indications and contraindications for nebulization in invasively ventilated ICU patients.
- National Survey (completed): Assessment of current practice, practice variation, and underlying beliefs across Dutch ICUs.
- Implementation Phase (ongoing): Introduction of the decision support tool in participating centers, combined with a structured assessment of barriers and facilitators using the MIDI framework. Findings are used to develop center-specific implementation toolboxes.
- Evaluation Phase: An evaluation of uptake, adherence, reduction of non-indicated nebulization, and changes in clinical practice over time after introduction of the decision support tool.
Study Population
ICU clinicians involved in nebulization decision-making and practice, including intensivists, ICU nurses, and ventilation practitioners.
Intervention
A consensus-based decision support tool (flowchart + onboarding materials), supplemented with centre-specific implementation strategies derived from MIDI findings.
Primary Outcome
- Proportion of indicated nebulizations among all nebulization events during the measurement periods.
Secondary Outcomes
- Barriers and facilitators to implementation (MIDI).
- Uptake and adherence of the decision support tool.
- Changes in indication, frequency, and practice after implementation.
- Development and use of centre-specific implementation toolboxes.
Documents
Study team
Steering committee
Participating centers
|
Amsterdam UMC, locatie AMC en VUmc, Amsterdam |
UMC Utrecht, Utrecht |
|
Maasstad ziekenhuis, Rotterdam |
Noord West Ziekenhuis, Alkmaar |
eCRF
The eCRF is built in Castor EDC, a program that can be reached from everywhere via the internet.
FAQ
Contact us

